What model of practice does EIT use?
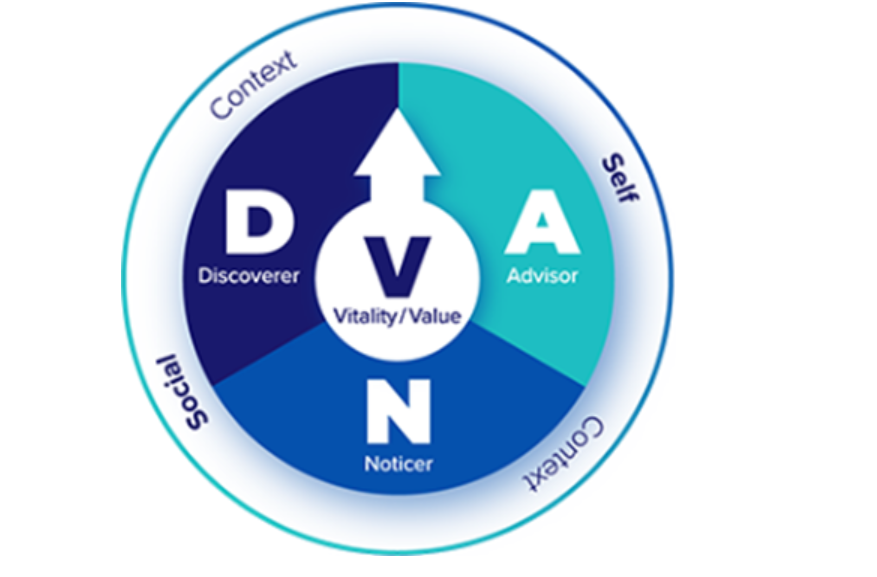
EIT Psychologists use an evidence-based model called DNA-V (Hayes & Ciarrochi, 2015 – see DNA-V Model of Psychological Flexibility | DNA-V International (dnav.international) for further information). DNA-V is a developmentally sensitive version of the Acceptance & Commitment Therapy (ACT; Hayes, Strosahl & Wilson, 1999; 2012) model. The model helps practitioners to support young people in developing a core set of psychological skills demonstrated through research to be fundamentally important for wellbeing, resilience and prosocial behaviour. For a few brief video clips introducing the DNA-V model, go to: DNA-V Video and Audio Resources (dnav.international)
DNA-V works on the following psychological skills:
- Discoverer (D) skills: The Discoverer represents behaviours related to exploring and testing the world. We use Discoverer skills to broaden our behavioural repertoires, try new things and assess how they work, find and create values and build strengths.
- Noticer (N) skills: Developing our Noticer skills allows us to connect with our feelings, our bodies and the physical signals coming in from the world around us. We all start life with this ability to notice. However, once we start verbalising and thinking symbolically, we can easily lose touch with our ability to notice and experience the world as a physical place.
- Advisor (A) skills: The Advisor is a metaphor for how humans use language to make sense of the world. It’s how we use our inner voice or self-talk to make sense of the past, form beliefs, evaluate ourselves, and predict the future. Thanks to the Advisor, we don’t have to rely on experience and trial and error to figure everything out. When using the DNA-V model, working in the Advisor space means developing a conscious and flexible relationship with our thoughts.
- Valuing (V) skills: In DNA-V, Values can be thought of as personal qualities we most want to express in our actions. Metaphorically, we can think of our Values as a compass that can help guide us through the storms and confusing times in life. Ultimately, everything in DNA-V aims to help young people connect with, and act in line with, their personal values.
- Flexible Self-View skills: Working within the Flexible Self-View space involves developing skills that enable flexible perspective-taking. This includes taking a view of oneself in different times and being able to connect with the idea of oneself as being an ever changing and ever growing being.
- Flexible Social-View skills: Working in the Flexible Social-View space involves developing skills that enable flexible perspective-taking, particularly with regard to our relationships with others and our place within our social world (Hayes & Ciarrochi, 2015).
The DNA-V model